paho-mqtt-c中的stack trace
前几天看paho-mqtt-c库源码的时候,看到一个FUNC_ENTRY用于记录函数调用栈信息,觉得还是很有意思的,在此阅读一下,并尝试将其转换为程序员工具库中的一员。
FUNC_ENTRY源码
首先可以先看看FUNC_ENTRY是什么:
#define FUNC_ENTRY StackTrace_entry(__func__, __LINE__, TRACE_MINIMUM)
void StackTrace_entry(const char* name, int line, enum LOG_LEVELS trace);
FUNC_ENTRY是StackTrace_entry函数的宏定义,传入的参数有当前的函数名和行号,这里的TRACE_MINIMUM源自于以下枚举,表示的是日志等级:
enum LOG_LEVELS {
INVALID_LEVEL = -1,
TRACE_MAXIMUM = 1,
TRACE_MEDIUM,
TRACE_MINIMUM,
TRACE_PROTOCOL,
LOG_ERROR,
LOG_SEVERE,
LOG_FATAL,
};
再来看下StackTrace_entry的实现:
nt setStack(int create)
{
int i = -1;
// 获取当前线程ID
thread_id_type curid = Paho_thread_getid();
my_thread = NULL;
// 遍历线程数组,判断线程数组是否有当前线程ID
for (i = 0; i < MAX_THREADS && i < thread_count; ++i)
{
if (threads[i].id == curid)
{
my_thread = &threads[i];
break;
}
}
// 如果线程数组没有当前线程ID的话,则初始化并填充线程数组
if (my_thread == NULL && create && thread_count < MAX_THREADS)
{
my_thread = &threads[thread_count];
my_thread->id = curid;
my_thread->maxdepth = 0; //调用最大深度
my_thread->current_depth = 0; //当前调用深度
++thread_count;
}
return my_thread != NULL; /* good == 1 */
}
void StackTrace_entry(const char* name, int line, enum LOG_LEVELS trace_level)
{
Paho_thread_lock_mutex(stack_mutex);
// 表示设置线程信息
if (!setStack(1))
goto exit;
if (trace_level != -1) //由上文可知这里为TRACE_MINIUM
// 根据日志等级记录当前调用栈信息
Log_stackTrace(trace_level, 9, my_thread->id, my_thread->current_depth, name, line, NULL);
// 记录当前调用栈的名字(函数名)
strncpy(my_thread->callstack[my_thread->current_depth].name, name, sizeof(my_thread->callstack[0].name)-1);
// 更新记录当前调用行号
my_thread->callstack[(my_thread->current_depth)++].line = line;
if (my_thread->current_depth > my_thread->maxdepth)
my_thread->maxdepth = my_thread->current_depth;
if (my_thread->current_depth >= MAX_STACK_DEPTH)
Log(LOG_FATAL, -1, "Max stack depth exceeded");
exit:
Paho_thread_unlock_mutex(stack_mutex);
}
StackTrace_entry做了几件事情:
- 设置/初始化当前线程信息:线程id、调用最大深度和当前调用深度;
- 根据日志等级记录当前调用栈信息;
- 更新记录当前调用函数名和行号、当前调用深度
现在来看下Log_stackTrace是如何实现的:
void Log_stackTrace(enum LOG_LEVELS log_level, int msgno, thread_id_type thread_id, int current_depth, const char* name, int line, int* rc)
{
traceEntry *cur_entry = NULL;
if (trace_queue == NULL)
return;
if (log_level < trace_settings.trace_level)
return;
Paho_thread_lock_mutex(log_mutex);
cur_entry = Log_pretrace(); // 从trace队列中取出一项
memcpy(&(cur_entry->ts), &now_ts, sizeof(now_ts));
cur_entry->number = msgno; // 消息编号,由上文得知为9
cur_entry->thread_id = thread_id; // 当前线程ID
cur_entry->depth = current_depth; //当前调用深度
strcpy(cur_entry->name, name); //当前调用函数名
cur_entry->level = log_level; // 日志等级TRACE_MINIUM
cur_entry->line = line; // 当前行号
if (rc == NULL)
cur_entry->has_rc = 0; // 没有返回码,设置为0
else
{
cur_entry->has_rc = 1;
cur_entry->rc = *rc;
}
Log_posttrace(log_level, cur_entry); // 提交到trace队列
Paho_thread_unlock_mutex(log_mutex);
}
Log_stackTrace做了几件事情:
- 从trace队列中取出一项,用来填充/记录调用栈信息;
- 记录调用栈信息到trace项中;
- 提交调用信息
我们进一步来看下两个核心函数的实现,即Log_pretrace和Log_posttrace:
static traceEntry* Log_pretrace(void)
{
traceEntry *cur_entry = NULL;
#if defined(GETTIMEOFDAY)
gettimeofday(&now_ts, NULL);
#else
ftime(&now_ts);
#endif
// 调整trace队列的大小到max trace的大小
if (trace_queue_size != trace_settings.max_trace_entries)
{
traceEntry* new_trace_queue = malloc(sizeof(traceEntry) * trace_settings.max_trace_entries);
if (new_trace_queue == NULL)
goto exit;
memcpy(new_trace_queue, trace_queue, min(trace_queue_size, trace_settings.max_trace_entries) * sizeof(traceEntry));
free(trace_queue);
trace_queue = new_trace_queue;
trace_queue_size = trace_settings.max_trace_entries;
// trace队列的开始索引或 指向下个数据的索引 比trace max大小要大
if (start_index > trace_settings.max_trace_entries + 1 ||
next_index > trace_settings.max_trace_entries + 1)
{
start_index = -1;
next_index = 0;
}
}
/* add to trace buffer */
cur_entry = &trace_queue[next_index];
if (next_index == start_index) /* means the buffer is full */
{
if (++start_index == trace_settings.max_trace_entries)
start_index = 0;
} else if (start_index == -1)
start_index = 0;
if (++next_index == trace_settings.max_trace_entries)
next_index = 0;
exit:
return cur_entry;
}
- 调整trace的大小为max;
- 把trace队列的指向下一个数据的索引取出来(地址);
- 更新开始索引和指向下个数据的索引
static char* Log_formatTraceEntry(traceEntry* cur_entry)
{
struct tm *timeinfo;
int buf_pos = 31;
#if defined(GETTIMEOFDAY)
timeinfo = localtime((time_t *)&cur_entry->ts.tv_sec);
#else
timeinfo = localtime(&cur_entry->ts.time);
#endif
// 加入当前时间信息
strftime(&msg_buf[7], 80, "%Y%m%d %H%M%S ", timeinfo);
#if defined(GETTIMEOFDAY)
snprintf(&msg_buf[22], sizeof(msg_buf)-22, ".%.3lu ", cur_entry->ts.tv_usec / 1000L);
#else
snprintf(&msg_buf[22], sizeof(msg_buf)-22, ".%.3hu ", cur_entry->ts.millitm);
#endif
buf_pos = 27;
msg_buf[6] = ' ';
if (cur_entry->has_rc == 2) // 由上文可知没有没有返回码,所以走不到这个分支
strncpy(&msg_buf[buf_pos], cur_entry->name, sizeof(msg_buf)-buf_pos);
else
{
// 取出trace项里边的消息编号和trace的日志等级
const char *format = Messages_get(cur_entry->number, cur_entry->level);
if (cur_entry->has_rc == 1)
snprintf(&msg_buf[buf_pos], sizeof(msg_buf)-buf_pos, format, cur_entry->thread_id,
cur_entry->depth, "", cur_entry->depth, cur_entry->name, cur_entry->line, cur_entry->rc);
else // 加入消息buf
snprintf(&msg_buf[buf_pos], sizeof(msg_buf)-buf_pos, format, cur_entry->thread_id,
cur_entry->depth, "", cur_entry->depth, cur_entry->name, cur_entry->line);
}
return msg_buf;
}
static void Log_output(enum LOG_LEVELS log_level, const char *msg)
{
if (trace_destination)
{
fprintf(trace_destination, "%s\n", msg);
// trace不是输出到标准输出的,比如说文件等,且写入行数比规定的最大行数要大,更新文件
if (trace_destination != stdout && ++lines_written >= max_lines_per_file)
{
fclose(trace_destination);
_unlink(trace_destination_backup_name); /* remove any old backup trace file */
rename(trace_destination_name, trace_destination_backup_name); /* rename recently closed to backup */
trace_destination = fopen(trace_destination_name, "w"); /* open new trace file */
if (trace_destination == NULL)
trace_destination = stdout;
lines_written = 0;
}
else
fflush(trace_destination);
}
if (trace_callback) // 有自定义的trace写入时的回调函数也在这里执行
(*trace_callback)(log_level, msg);
}
static void Log_posttrace(enum LOG_LEVELS log_level, traceEntry* cur_entry)
{
if (((trace_output_level == -1) ? log_level >= trace_settings.trace_level : log_level >= trace_output_level))
{
char* msg = NULL;
if (trace_destination || trace_callback)
msg = &Log_formatTraceEntry(cur_entry)[7];
Log_output(log_level, msg);
}
}
- 格式化trace记录信息;
- 输出到标准输出或者文件,如若需要则更新输出所在文件
源码总结
FUNC_ENTRY的大致调用流程如下:
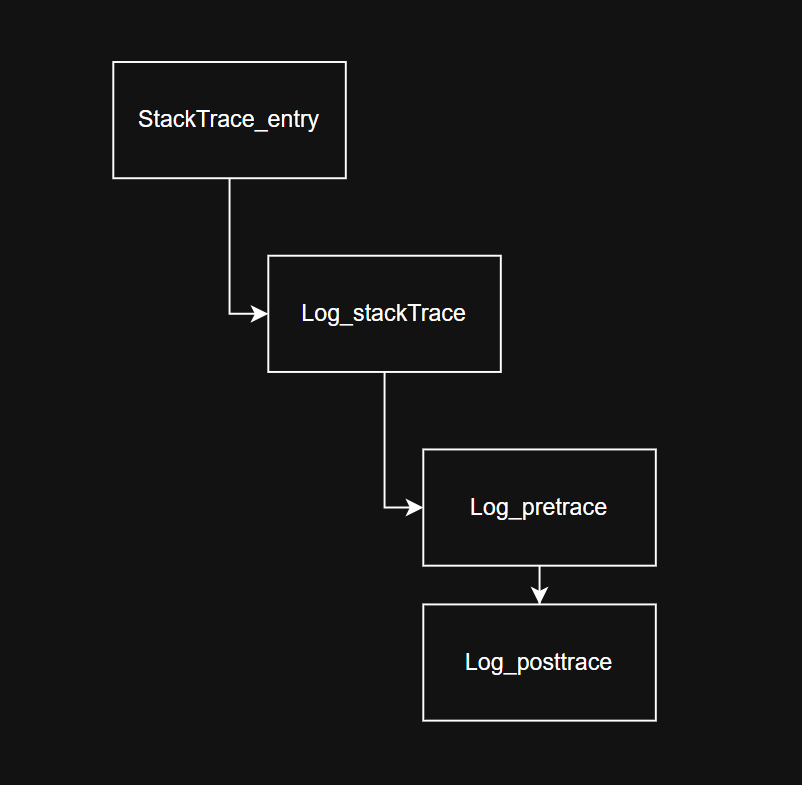
收集
- 记录函数调用栈信息可以提供宏封装;
- 规定一个供记录函数调用栈信息的日志等级,在日志系统中解耦处理;
- 可记录线程ID、函数名、行号,格式化输出到标准输出或者指定文件时,可加上时间信息;
- 可使用线程数组的方式记录调用栈的深度信息,定义一个结构体用于记录当前线程ID、当前调用深度和最大深度;
- 函数调用栈信息可使用日志组件或自定义日志系统,将调用栈信息用循环队列以节点的方式进行存储;
- 注意线程安全问题:在涉及修改可能会被多个线程同时使用的数据结构的信息时,要加对应的锁(注意锁的粒度)